Few terms that you need to know firstPhoneticsThe scientific study of speech process and analysis of sound.
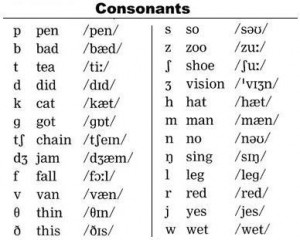
PhonemeThe unit of sound, like; /g/, /k/, /t/ etc. PhonologyPractical use of phonetics and study of sound system. LexiconDictionary.Entry or LexemeThe word of which you see the meanings in dictionary. Consonants, as explained in previous chapter, are those sounds which are pronounced / uttered by the touch of two organs. More explanation you will see below under origins of sounds. Below is the chart of all the consonants.
Whenever you open a dictionary one thing which is right at the start and unfortunately mostly neglected is the pronunciation guide, quite like as the chart below. We are usually more concerned about the meanings than anything else.
If you look at the chart you see there are three columns which are distributed as follows; First column: Contains phonemes, a unit of sound. Second column: Contains words that use the phoneme of the first column. Third column: Contains transcription. Transcription is phonological presentation of the sound of any word. Origins of soundsThere are different organs in vocal tract that produce consonant sound and they are explained as follows; Lips Sounds with respect to originSound is explained with respect to its origin and since consonants are pronounced by the touch of two organs in vocal tract so the origin means those two organs. See the explanation below. BilabialBilabial sounds are those which are uttered by the touch of two lips, like; /b/ and /p/. LabiodentalsThose sounds which are uttered by the touch of lower lip with upper teeth, like; /f/. AlveolarThe sounds that are pronounced by the touch
of tongue with teeth ridge (alveolar ridge), like; /th-
sound/and / PalatalThe sounds that are pronounced by the touch
of tongue with hard palate, like; / VelarThe sounds pronounced by the touch of tongue with soft palate, like; /k/ and /g/. GlottalThe sound uttered from glottis, like, /h/ The symbol of glottal /h/ is used when any voiceless consonant is aspirated. Aspiration is audible and forceful release of breath, like; ph, Kh. Some other kinds of consonantsPlosivesPlosives are those consonant sound which are pronounced by sudden release of air, like; /p/, /b/, /k/, /g/, /th- sound/and /th- sound2/. FricativesSuch consonant sounds that give hissing effect, like; /f/ and /z/. NasalSounds pronounced from the nasal cavity, like; /n/, /m/ and /ing-sound/. /ing-sound/ is the sound of ing that always comes at the end of present participle like, cooking, managing, breathing etc. AffricativesThe sounds that are pronounced by sudden release of air-stream with hissing friction, like; /j-sound/and /ch-sound/. Voiced and voiceless consonantsIt might be something strange that all the sound is actually voiced at the same time. But voiced here means the vibration in the vocal cords. Any consonant that creates vibration in vocal cords is called voiced otherwise it is voiceless. Now look at two consonants; /b/ and /p/. Just pronounce them and you will know. When you pronounce /p/ it is slight and no vibration in vocal cords is felt whereas if you pronounce /b/ it causes vibration.
How to feel the vibration in vocal cords?In order to feel vibration in vocal cords you can adopt two ways; Block your ears with the palms of your
hand and pronounce /p/ and /b/. in /b/ you will feel some
sort of vibration in vocal cords. In short while pronouncing voiced consonants the vocal cords are involved whereas in voiceless there is glottal stop. The glottis is blocked and the air-stream in mouth suddenly comes out. Watch the video |